Informations
Solution ID
Description of solution
The Kaunertal Valley in western Austria is experiencing glacier retreat, and the southern part of the valley, the ‘Gepatschferner’ glacier, is one of the fastest melting glaciers in Austria. This glacier retreat leaves unconsolidated sediments in steep lateral moraines exposed to erosion and subsequently rock fall, debris flows, and shallow landslides decreasing the slope stability in the proglacial. The Kaunertal pro glacial area will serve as a concept case where climatic changes, such as the increase in frequency and severity of extreme events, impose strong threats to the region.
The targets of the measures in the Kaunertal Valley are:
- testing the potential of high alpine plant species in reducing erosion
- identify microbes with the ability to assist the plants in establishing in areas prone to soil loss
Through the H2020 project PHUSICOS the stabilizing effect of vegetation and the growth-promoting effects of bacteria to enhance plant traits that most strongly contribute to slope stability, exclusively applying autochthonous species without introducing external species and microbes into the area, are demonstrated.
The work has been performed in the laboratory and a number of test plots at various locations in the Kaunertal Valley.
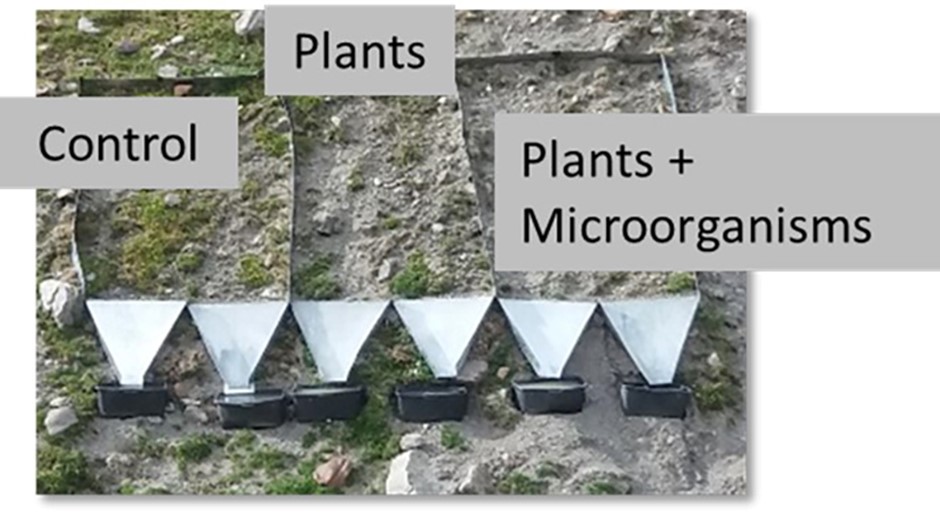
Each installation had three 2x3 m plots; a control plot with nothing done, a plot treated with plant seeds only, and a third plot with a mixture of seeds and microorganisms. Runoff has been monitored from all plots.
Focus is on plants with large leaf surfaces and a large root system since these traits are considered to be most effective against soil erosion. Many different seed mixtures and seed-bacteria mixtures have been tested, and it was found that all seed mixtures lead to an increase in vegetation cover and reduction in erosion, and the addition of bacteria led to a further reduction in erosion in the test plots.
Implementation at different sites, totaling an area of ca. 10.000 m2, has now been done, but results will not be available until the growth season of 2023 (outside PHUSICOS).
Main results of the test site activities before large-scale implementation include the following:
- The critical plant coverage for reducing erosion is ca. 30%, whereas a coverage of >75% almost eliminates the erosion in the test plots (measured as sediment yield from the plots)
- Campanula Barbata ('bearded bellflower') was found to be the most suitable plant, as it responded most significantly with changes in erosion by effective trait development through microbe interaction. However, functionally diverse plant communities seem to be most effective in reducing the erosion and to enrich the microbial composition
- The seed mixture applied to the test sites led to increased vegetation cover at all test sites, both with and without microbiome. At 44% of the sites a statistically significant increase of vegetation cover was achieved in plots with mixed-in microbes compared to those without microbes added.
Keywords
Actors
- The innovative research project have been initiated through the H2020 project PHUSICOS
- Implementation site monitoring will be happening outside PHUSICOS and are provided by the University of Vienna and the Paris Lodron University of Salzburg
Temporal aspects
Others
https://phusicos.eu/case_study/kaunertal-valley-austria/
